Prostate Cancer
WHAT IS THE PROSTATE?
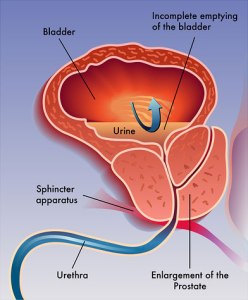
Just men have a prostate. It is a minute gland that sits below the bladder near the rectum. It environs the urethra, the way in the penis during which urine and semen pass. The prostate organ is an element of the male reproductive system. It produces most of the liquid that makes up semen that enriches sperm. The prostate is frequently described as being the size of a walnut and it is usual for it to grow as men age. The prostate needs the male hormone testosterone to grow and enlarge. At times this can cause problems, such as difficulty urinating. These harms are common in older men and not always symptoms or signs of cancer.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
In the early stages, here may be no symptoms. Within the later stages, some symptoms of prostate cancer might include:
- Feeling the common or sudden need to urinate
- Finding it hard to urinate (for example, trouble starting or not being able to urinate when the feeling is there or poor urine flow)
- Distress when urinating
- Ruling blood in urine or semen
- Pain in the lower back, higher thighs or hips.
The particular symptoms may not mean you have prostate cancer, but if you experience any of them, go and see your doctor.
WHAT ARE THE RISK FACTORS?
Factors that are most powerfully linked to an enlarged chance of developing prostate cancer:
Age: Prostate cancer is an age-dependent syndrome, which means the chance of growing it increases with age. The risk of receiving prostate cancer by the age of 75 is 1 in 7 men. In the age of 85, this increases to 1 in 5.
Family history: But you have a first-degree male relative with prostate cancer, you have a higher chance of raising it than men with no such history. The risk increases over if more than one male relative has prostate cancer. Risks are too higher for men whose male relatives were diagnosed when young.
THE STAGING SYSTEM FOR PROSTATE CANCER IS:
STAGE I: cancer involves only one lobe of the prostate.
STAGE II: The cancer is recovered or involves both lobes of the prostate. But, it has not spread outside the prostate.
STAGE III: cancer has spread outside the prostate connecting adjacent organs such as the seminal vesicles.
STAGE IV: cancer has extended to the bones and other parts of the body.
Another system for risk assessment of prostate cancer is the D’Amico System, which combines the PSA level, the Gleason score on the basis of biopsy and clinical stage based on radiological examination.
HOW IS PROSTATE CANCER DETECTED AND DIAGNOSED?
A doctor will frequently do a blood test and/or physical examination to test the health of the prostate.
Blood check (Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) test): The result shows whether there is an increase in this specific protein. Depending on the product, you might need further investigation with a specialist. A high PSA test outcome does not necessarily mean cancer. Prostate diseases other than cancer can as well cause a higher than normal PSA level.
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE): Since of where the prostate is located, the doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to check the mass of the prostate and assess if there are any abnormalities. A normal DRE effect does not rule out prostate cancer.
DIAGNOSIS
But your tests prove you may be at risk of prostate cancer, the next step is a biopsy. A biopsy is the only method a firm diagnosis of prostate cancer can be made. A urologist removes small samples of tissue from your prostate, using very thin, hollow needles guided by an ultrasound. The prostate is also accessed through the rectum (transrectal) or the perineum (transperineal), which is the area between the anus and the scrotum. A biopsy is typically done as an out-patient system and the doctor will likely advise a course of antibiotics afterward to reduce the chance of infection. The tissue is sent to a pathologist to recognize whether the cells are malignant (cancerous) or benign (not cancerous).
Dr. Suraj Lunavat is an expert in the Enlarge Prostate Treatment in Pune , Kidney Stone Treatment with Laser technique, Urinary tract infection treatment, Urinary cancer diagnosis and treatment, treatment of female urinary problems, treatment of urinary and bladder stones and treatment for urinary obstruction With the 10 years of experience in the industry He deals with the surgical aspects of diseases of the kidney, bladder, and prostate.