Is Your Prostate Enlarged? 8 Facts You Should Know.
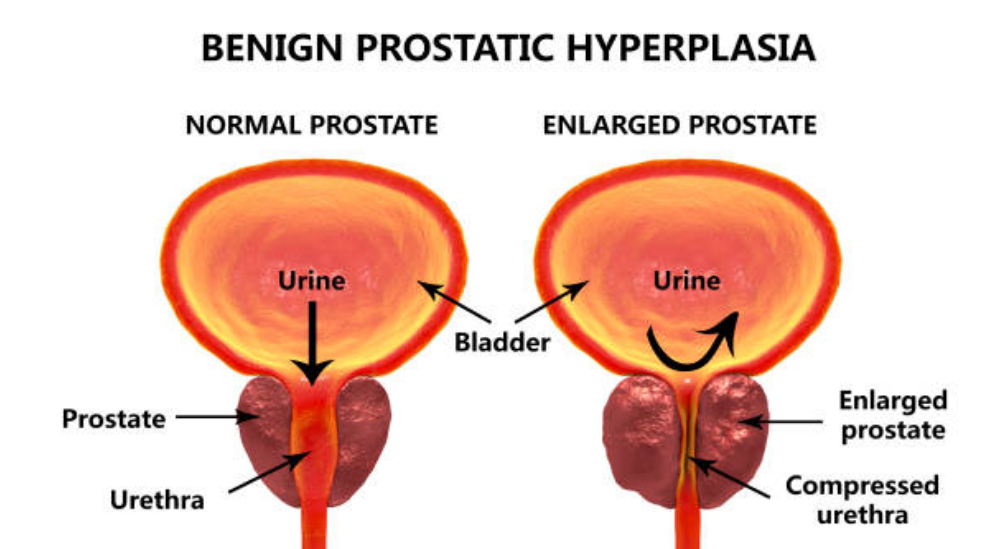
A body is the most important to a human. We can hide our right age from people but can not ignore the main problems that we will face when we get older. Enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is the common problem that men face in the age of 60 and above.
So, if you want to know about it in brief here are the 8 facts.
Common problem: It is to be said that BPH is the most common problem for the older men. There is not any kind of proof that decides the causes of it but medical professionals agree that ageing and testosterone is the main thing that influences the most. But here is a thing that can’t develop BPH in men only when testicles will remove at a very young age.
Can leads to a serious issue: If people will ignore it and won’t give proper attention towards it then it can lead to a serious problem. Because of men that urinary problems are common in the old age and therefore they ignore the problem. But if it left untreated then it causes a problem for one’s health.
Lead to a stone problem: when it comes to the bladder then it will cause the infection in stagnant urine. By which the urine will collect and get crystalised that can lead to the stone problem. So, well treatment is important.
BPH does not to cancer: people usually believe that it also can lead to cancer but it cannot. Prostate cancer is a very different disease as compared to BPH. The BPH can be treated but prostate cancer can’t. So, we can’t compare it with each other.
Leads to kidney damage: kidney is connected to the bladder and due to increased pressure over the kidney from an overworked bladder can really damage their kidneys. And this is a serious kinda problem. So proper treatment is important.
Ignorance can also to urinary retention: when it comes to full of bladder then you can’t even urine at all and at that time you need and emergency help and treatment. And it should never be ignored by one.
Can leads to visible blood in the urine: if it would not get well treated it can cause gross hematuria which means the blood can be seen by naked eyes in urine and it should not be ignored.
For More Details:
Visit Best Urologist in Pune | Dr. Suraj Lunavat